If you have already configured session 1 with a local or remote destination, you can enter the vlan or vid monitorinterface command without additional parameters for traffic-selection criteria and session number to configure mirroring for all inbound and outbound traffic on the specified VLAN or port interfaces in session 1 with the preconfigured destination.port monitor
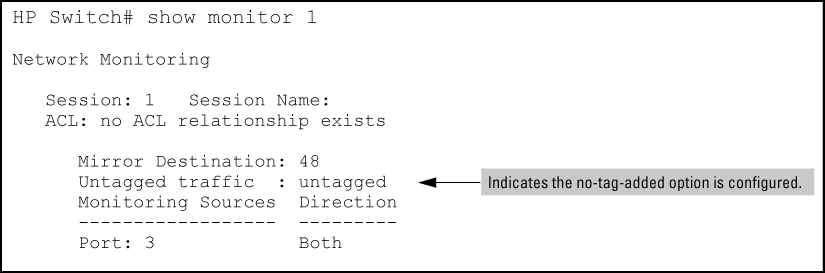
Although a VLAN tag is added (by default) to the mirrored copy of untagged outbound packets to indicate the source VLAN of the packet, it is sometimes desirable to have mirrored packets look exactly like the original packet. The no-tag-added parameter gives you the option of not tagging mirrored copies of outbound packets, as shown in Mirroring commands with the no-tag-added option and Displaying a mirror session configuration with the no-tag-added option.
The MIB object hpicfBridgeDontTagWithVlan is used to implement the no-tag-added option, as shown below:
hpicfBridgeDontTagWithVlan OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX INTEGER
{
enabled(1),
disabled(2)
}
MAX-ACCESS read-write
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"This oid mentions whether VLAN tag is part of the
mirror'ed copy of the packet. The value ‘enabled'
denotes that the VLAN tag shouldn't be part
of the mirror'ed copy; ‘disabled' does put
the VLAN tag in the mirror'ed copy. Only one
logical port is allowed.
This object is persistent and when written
the entity
SHOULD save the change to non-volatile storage."
DEFVAL { 2 }
::= { hpicfBridgeMirrorSessionEntry 2 }
The following conditions apply for the no-tag-added option:
-
The specified port can be a physical port, trunk port, or mesh port.
-
Only a single logical port (physical port or trunk) can be associated with a mirror session when the
no-tag-addedoption is specified. No other combination of ACL mirroring, VLAN mirroring, or port mirroring can be associated with the mirror session. If more than one logical port is specified, the following error message is displayed:Cannot monitor more than one logical port with no-tag-added option
-
If a port changes its VLAN membership and/or untagged status within the VLAN, the "untagged port mirroring" associated with that port is updated when the configuration change is processed.
-
Only four ports or trunks can be monitored at one time when all four mirror sessions are in use (one logical port per mirror session) without VLAN tags being added to a mirrored copy.
-
The
no-tag-addedoption can also be used when mirroring is configured with SNMP. -
A VLAN tag is still added to the copies of untagged packets obtained via VLAN-based mirroring.
Deprecation of ACL-based traffic selection
In release K.14.01 or greater, the use of ACLs to select inbound traffic in a mirroring session has been replaced with classifier-based mirroring policies.
The following commands have been deprecated:
After you install and boot release K.14.01 or greater, ACL-based local and remote mirroring sessions configured on a port or VLAN interface are automatically converted to classifier-based mirroring policies.
Use the monitor mac mirror command at the global configuration level to apply a source and/or destination MAC address as the selection criteria used in a local or remote mirroring session.
While classifier-based mirroring allows you to mirror traffic using a policy to specify IP addresses as selection criteria, MAC-based mirroring allows you monitor switch traffic using a source and/or destination MAC address. You can apply MAC-based mirroring in one or more mirroring sessions on the switch to monitor:
MAC-based mirroring is useful in HP Switch Network Immunity security solutions that provide detection and response to malicious traffic at the network edge. After isolating a malicious MAC address, a security administrator can mirror all traffic sent to and received from the suspicious address for troubleshooting and traffic analysis.
The MAC address that you enter with the monitor mac mirror command is configured to select traffic for mirroring from all ports and learned VLANs on the switch. Therefore, a suspicions MAC address used in wireless applications can be continuously monitored as it re-appears in switch traffic on different ports or VLAN interfaces.
You can configure MAC-based mirroring from the CLI or an SNMP management station and use it to mirror:
-
All inbound and outbound traffic from a group of hosts to one destination device.
-
Inbound and/or outbound traffic from each host to a different destination device.
-
Inbound and outbound traffic from all monitored hosts separately on two destination devices: mirroring all inbound traffic to one device and all outbound traffic to another device.
Restrictions
The following restrictions apply to MAC-based mirroring:
-
Up to 320 different MAC addresses are supported for traffic selection in all mirroring sessions configured on the switch.
-
A destination MAC address is not supported as mirroring criteria for routed traffic, because in routed packets, the destination MAC address is changed to the next-hop address when the packet is forwarded. Therefore, the destination MAC address that you want to mirror will not appear in routed packet headers.
This restriction also applies to the destination MAC address of a host that is directly connected to a routing switch. (Normally, a host is connected to an edge switch, which is directly connected to the router.)
To mirror routed traffic, we recommend that you use classifier-based policies to select IPv4 or IPv6 traffic for mirroring, as described in About selecting inbound traffic using advanced classifier-based mirroring.
-
On a switch, you can use a MAC address only once as a source MAC address and only once as a destination MAC address to filter mirrored traffic.
For example, after you enter the following commands:
monitor mac 111111-222222 src mirror 1monitor mac 111111-222222 dest mirror 2The following commands are not supported:
monitor mac 111111-222222 src mirror 3monitor mac 111111-222222 dest mirror 4In addition, if you enter the
monitor mac 111111-222222 both mirror 1command, you cannot use the MAC address111111-222222in any othermonitor mac mirrorconfiguration commands on the switch. -
To re-use a MAC address that has already been configured as a source and/or destination address for traffic selection in a mirror session, you must first remove the configuration by entering the
noform of the command and then re-enter the MAC address in a newmonitor mac mirrorcommand.For example, if you have already configured MAC address
111111-222222to filter inbound and outbound mirrored traffic, and you decide to use it to filter only inbound traffic in a mirror session, you could enter the following commands:monitor mac 111111-222222 both mirror 1 -
A mirroring session in which you configure MAC-based mirroring is not supported on a port, trunk, mesh, or VLAN interface on which a mirroring session with a classifier-based mirroring policy is configured.
In software release K.14.01 or greater, in addition to the traffic selection options described in Configure the monitored traffic in a mirror session, traffic mirroring supports the use of advanced classifier-based functions that provide:
-
A finer granularity for selecting the inbound IP traffic that you want to mirror on an individual port or VLAN interface (instead of mirroring all inbound traffic on the interface)
-
The ability to re-use the same traffic classes in different software-feature configurations; for example, you can apply both a QoS rate-limiting and mirroring policy on the same class of traffic.
Deprecation of ACL-based traffic selection
In software release K.14.01 or greater, advanced classifier-based policies replace ACL-based traffic selection in mirroring configurations.
Like ACL-based traffic-selection criteria, classifier-based service policies apply only to inbound traffic flows and are configured on a per-port or per-VLAN basis. In a mirroring session, classifier-based service policies do not support:
Classifier-based mirroring is not designed to work with other traffic-selection methods in a mirroring session applied to a port or VLAN interface:
-
If a mirroring session is already configured with one or more traffic-selection criteria (MAC-based or all inbound and/or outbound traffic), the session does not support the addition of a classifier-based policy.
-
If a mirroring session is configured to use a classifier-based mirroring policy, no other traffic-selection criteria (MAC-based or all inbound and/or outbound traffic) can be added to the session on the same or a different interface.
Classifier-based mirroring policies provide greater precision when analyzing and debugging a network traffic problem. Using multiple match criteria, you can finely select and define the classes of traffic that you want to mirror on a traffic analyzer or IDS device.