Traffic forwarding
After an MPLS TE tunnel is established, traffic is not forwarded on the tunnel automatically. You must direct the traffic to the tunnel by using one of the following methods:
Static routing
You can direct traffic to an MPLS TE tunnel by creating a static route that reaches the destination through the tunnel interface. This is the easiest way to implement MPLS TE tunnel forwarding. When traffic to multiple networks is to be forwarded through the MPLS TE tunnel, you must configure multiple static routes, which are complicated to configure and difficult to maintain.
For more information about static routing, see Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.
Automatic route advertisement
You can also configure automatic route advertisement to forward traffic through an MPLS TE tunnel. Automatic route advertisement distributes the MPLS TE tunnel to the IGP (OSPF or IS-IS), so the MPLS TE tunnel can participate in IGP routing calculation. Automatic route advertisement is easy to configure and maintain.
Automatic route advertisement can be implemented by using the following methods:
IGP shortcut—Also known as AutoRoute Announce. It considers the MPLS TE tunnel as a link that directly connects the tunnel ingress node and the egress node. Only the ingress node uses the MPLS TE tunnel during IGP route calculation.
Forwarding adjacency—Considers the MPLS TE tunnel as a link that directly connects the tunnel ingress node and the egress node, and advertises the link to the network through an IGP. Every node in the network uses the MPLS TE tunnel during IGP route calculation.
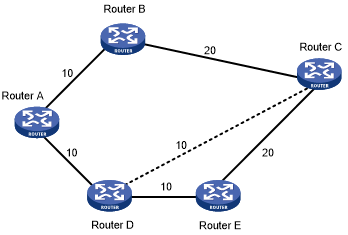
As shown in Figure 23, an MPLS TE tunnel exists from Router D to Router C. IGP shortcut enables only the ingress node Router D to use the MPLS TE tunnel in the IGP route calculation. Router A cannot use this tunnel to reach Router C. With forwarding adjacency enabled, Router A can learn this MPLS TE tunnel and transfer traffic to Router C by forwarding the traffic to Router D.
Figure 23: IGP shortcut and forwarding adjacency diagram