CRLSP establishment using PCE path calculation
On an MPLS TE network, a Path Computation Client (PCC), usually an LSR, uses the path calculated by Path Computation Elements (PCEs) to establish a CRLSP through RSVP-TE.
Basic concepts
PCE—An entity that can calculate a path based on the TEDB, bandwidth, and other MPLS TE tunnel constraints. A PCE can provide intra-area or inter-area path calculation. A PCE can be manually specified on a PCC or automatically discovered through the PCE information advertised by OSPF TE.
PCC—A PCC sends a request to PCEs for path calculation and uses the path information returned by PCEs to establish a CRLSP.
PCEP—Path Computation Element Communication Protocol. PCEP runs between a PCC and a PCE, or between PCEs. It is used to establish PCEP sessions to exchange PCEP messages over TCP connections.
PCE path calculation
PCE path calculation has the following types:
EPC—External Path Computation. EPC path calculation is performed by one PCE. It is applicable to intra-area path calculation.
BRPC—Backward-Recursive PCE-Based Computation. BRPC path calculation is performed by multiple PCEs. It is applicable to inter-area path calculation.
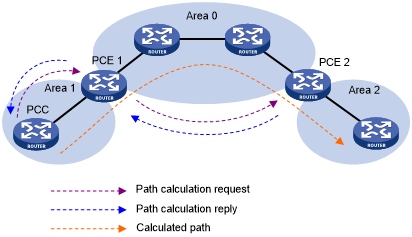
As shown in Figure 22, PCE 1 is the ABR that can calculate paths in Area 0 and Area 1. PCE 2 is the ABR that can calculate paths in Area 1 and Area 2. The CRLSP that PCC uses to reach a destination in Area 2 is established as follows:
PCC sends a path calculation request to PCE 1 to request the path to the CRLSP destination.
PCE 1 forwards the request to PCE 2.
PCE 1 cannot calculate paths in Area 2, so it forwards the request to PCE 2, the PCE responsible for Area 2 that contains the CRLSP destination.
After receiving the request from PCE 1, PCE 2 calculates potential paths to the CRLSP destination and sends the path information back to PCE 1 in a reply.
PCE 1 uses the local and received path information to select an end-to-end path for the PCC to reach the CRLSP destination, and sends the path to PCC as a reply.
PCC uses the path calculated by PCEs to establish the CRLSP through RSVP-TE.
Figure 22: BRPC path calculation