LDP FRR
A link or router failure on a path can cause packet loss until LDP establishes a new LSP on the new path. LDP FRR enables fast rerouting to minimize the failover time. LDP FRR is based on IP FRR and is enabled automatically after IP FRR is enabled.
You can use one of the following methods to enable IP FRR:
Configure an IGP to automatically calculate a backup next hop.
Configure an IGP to specify a backup next hop by using a routing policy.
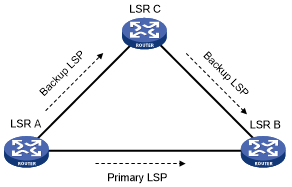
As shown in Figure 14, configure IP FRR on LSR A. The IGP automatically calculates a backup next hop or it specifies a backup next hop through a routing policy. LDP creates a primary LSP and a backup LSP according to the primary route and the backup route calculated by IGP. When the primary LSP operates correctly, it forwards the MPLS packets. When the primary LSP fails, LDP directs packets to the backup LSP.
When packets are forwarded through the backup LSP, IGP calculates the optimal path based on the new network topology. When IGP route convergence occurs, LDP establishes a new LSP according to the optimal path. If a new LSP is not established after IGP route convergence, traffic forwarding might be interrupted. As a best practice, enable LDP-IGP synchronization to work with LDP FRR to reduce traffic interruption.
Figure 14: Network diagram for LDP FRR