Remote Copy terminology
- Remote Copy group
A Remote Copy virtual volume set of one or more virtual volumes to be replicated to another system. I/O consistency is guaranteed across the virtual volumes in a Remote Copy group.
- Primary system
The HPE 3PAR StoreServ Storage system which contains the Remote Copy group from which data is replicated to a secondary system. The primary system takes write I/Os from a server for the virtual volumes in a Remote Copy group and sends that data to a secondary system.
A primary system can also be referred to as the source or local system.
- Secondary system
The storage system which contains the Remote Copy group to which data is replicated. The secondary system receives replication data from the primary system and applies that data to the virtual volumes in a Remote Copy group.
The secondary system can also be referred to as the target or remote system. Target is often used in other documentation to represent the secondary system.
- Primary-rev
Following a failover, the secondary system takes on the role of primary-rev indicating that it is now the primary storage system as the result of a failover.
- Secondary-rev
Following a failover, the primary system takes on the role of secondary-rev indicating that it is now the secondary storage system as the result of a failover.
- Source system
The system that generates the data and sends it to the target. Because the primary and secondary roles can change, Remote Copy uses the term source system to refer to a storage system in a linked pair of storage systems. The source system is the primary or primary-rev system.
- Target system
The system that receives the replicated data. Because the primary and secondary roles can change, Remote Copy uses the term target system to refer to the other storage system in a linked pair of storage systems.
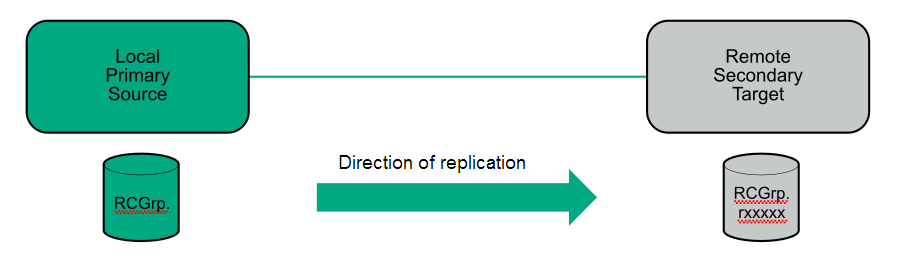
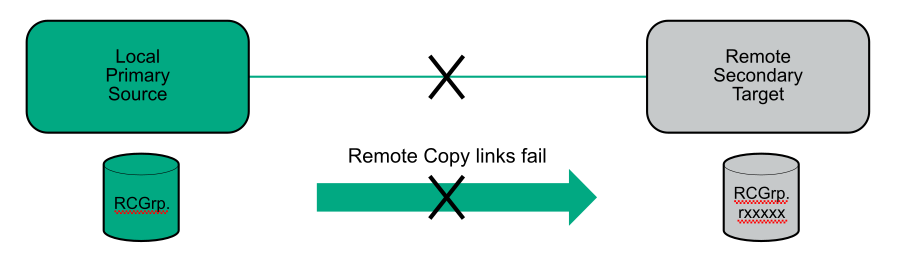
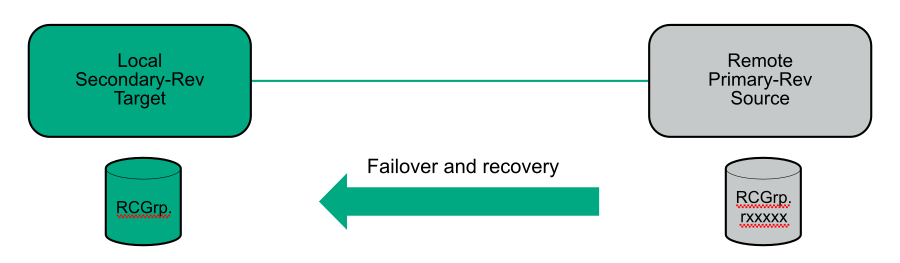

In a failover, the original direction of replication is restored after recover and restore actions are completed. In a reverse, the original direction of replication is restored when the primary-rev system becomes the primary and the secondary-rev system becomes the secondary.