Assigning the following DSCP policies to the packets that match the specified global IP-device classifiers:
| IP address | DSCP Policy | |
|---|---|---|
| DSCP codepoint | 802.1p priority | |
| 10.28.31.1 | 000111 | 7 |
| 10.28.31.130 | 000101 | 5 |
| 10.28.31.100/24 | 000010 | 1 |
| 2001:db8:2:1:212:79ff:fe88:a100 | 000101 | 3 |
| 2001:db8:3:3::/64 | 000010 | 1 |
-
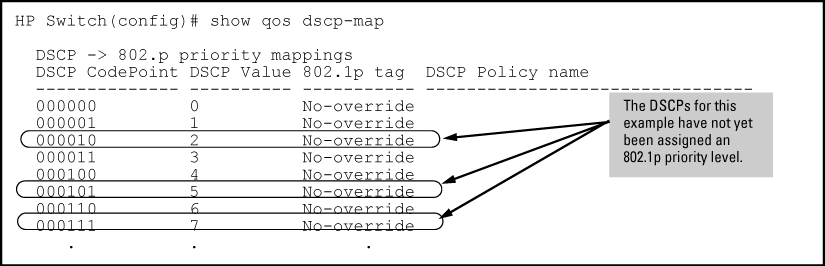
Determine whether the DSCP codepoints that you want to use to mark matching packets already have an 802.1p priority assigned, which could indicate use by existing applications (
show qos dscp-mapcommand). This is not a problem if the configured priorities are acceptable for all applications that use the same DSCP.Note that a DSCP codepoint must have an associated priority before you can use it to mark matching packets.
-
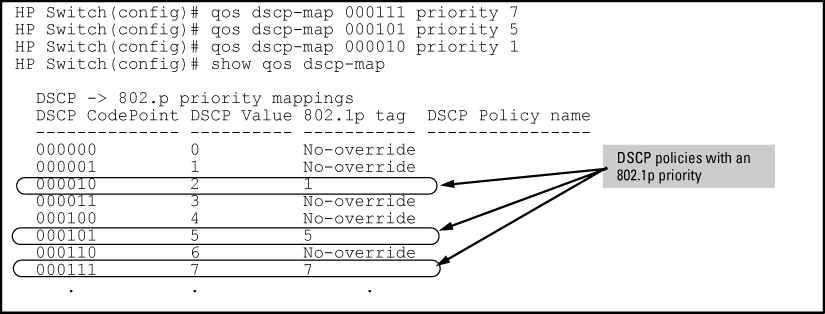
Configure the priorities for the DSCPs you want to use to mark packets.
-
Assign the DSCP policies to the specified IP-device addresses and display the result.
HP Switch(config)#: qos device-priority 10.28.31.1 dscp 000111 HP Switch(config)#: qos device-priority 10.28.31.130 dscp 000101 HP Switch(config)#: qos device-priority ipv4 10.28.32.100/24 dscp 000010 HP Switch(config)#: qos device-priority 2001:db8:2:1:212:79ff:fe88:a100 dscp 000 HP Switch(config)#: qos device-priority ipv6 2001:db8:3:3/64 dscp 000010 HP Switch(config)#: show qos device-priority Device priorities Device Address Apply rule | DSCP Priority -------------------------------------------- ---------- + ------ ----------- 10.28.31.1 Priority | 000111 7 10.28.31.130 Priority | 000101 5 10.28.32.100/24 Priority | 000010 1 2001:db8:2:1:212:79ff:fe88:a100 Priority | 000101 3 2001:db8:3:3/64 Priority | 000010 1
The switch applies the DSCP policies in Assigning 802.1p priorities to the selected DSCPs to IP packets with the specified IP addresses and subnet masks (source or destination) received in the switch. The switch manages the packets as follows:
-
Overwrites the original DSCPs in the selected packets with the new DSCPs specified in the above policies.
-
Assigns the 802.1p priorities in the above policies to the appropriate packets.
This global QoS packet-marking option assigns a previously configured DSCP policy (codepoint and 802.1p priority) to outbound IP packets having the specified IP address or subnet mask in the source or destination field of their packet header. The switch:
-
Selects an incoming IPv4 or IPv6 packet on the basis of the source or destination IP address or subnet mask it carries.
-
Overwrites the DSCP in matching packets with the globally configured DSCP codepoint, and assigns the 802.1p priority associated with the new DSCP.
-
Forwards the packet through the appropriate outbound port queue.
This global QoS packet-marking option assigns a previously configured or default DSCP policy (codepoint and 802.1p priority) to TCP or UDP packets having the specified port number or range of port numbers. When assigning a DSCP policy, the switch performs the following actions:
The following procedure creates a DSCP policy for IP packets carrying the selected TCP or UDP port-number classifier.
-
Identify the TCP or UDP port-number classifier you want to use for assigning a DSCP policy.
-
Determine the DSCP policy for packets carrying the selected TCP or UDP port number or range of port numbers.
-
If necessary, use the
qos dscp-mapcodepointpriority0 - 7
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.gif)
NOTE: Prerequisite: A DSCP codepoint must have a preconfigured 802.1p priority (0 - 7) before you can use the codepoint to mark matching packets. If a codepoint you want to use shows
No-overrideshow qos dscp-map), you must first configure a priority for the codepoint before proceeding (qos dscp-map priority).
Syntax:
Options
This command is required only if an 802.1p priority is not already assigned to the specified
codepointValid values for a DSCP codepoint are as follows:
-
A binary value for the six-bit codepoint from
000000to111111. -
A decimal value from
0(low priority) to63(high priority) that corresponds to a binary DSCP bit set -
An ASCII standard (hexadecimal) name for a binary DSCP bit set
af11(001010)af42(100100)af12(001100)af43(100110)af13(001110)ef(101110)af21(010010)cs1(001000) = precedence 1af22(010100)cs2(010000) = precedence 2af23(010110)cs3(011000) = precedence 3af31(011010)cs4(100000) = precedence 4af32(011100)cs5(101000) = precedence 5af33(011110)cs6(110000) = precedence 6af41(100010)cs7(111000) = precedence 7default(000000)Enter ? to display the list of valid codepoint entries.
When the switch applies the specified DSCP policy to a packet, the priority determines the packet's queue in the outbound port to which it is sent. If the packet leaves the switch on a tagged port, it carries the 802.1p priority with it to the next downstream device. For IP packets, the DSCP will be replaced by the codepoint specified in this command.
Default: No-override for most codepoints.
-
-
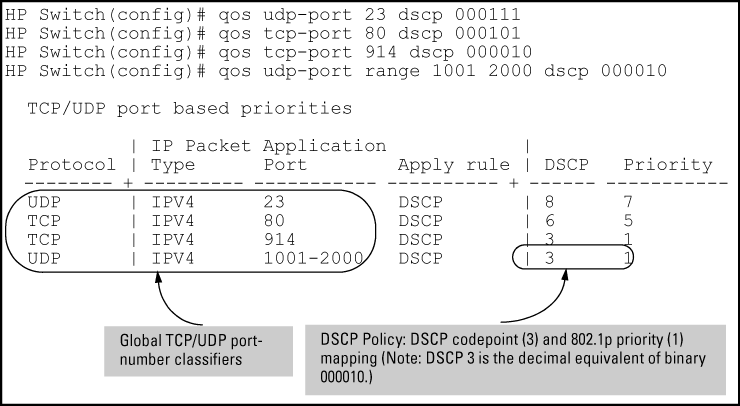
Configure the switch to assign the DSCP policy to packets with the specified TCP or UDP port number or range of port numbers.
Syntax:
qos[udp-port|tcp-portipv4|ipv6|ip-all]
[port-number|rangestart end] dscpcodepointAssigns a DSCP policy to outbound packets having the specified TCP or UDP application-port number or port range, and overwrites the DSCP in these packets with the assigned
codepointvalue, where:-
ipv4marks only IPv4 packets (default). -
ipv6marks only IPv6 packets. -
ip-allmarks all IP traffic (both IPv4 and IPv6 packets). -
port-numberspecifies a TCP/UDP port-number from 1 to 65535. -
range start endspecifies a range of TCP/UDP ports. If you specify a range, the minimum port number must precede the maximum port number in the range. -
dscp codepointoverwrites the DSCP codepoint in the IPv4 ToS byte or IPv6 Traffic Class byte of matching packets with the specified value.Valid values for the DSCP codepoint are as follows:
-
A binary value for the six-bit codepoint from
000000to111111. -
A decimal value from
0(low priority) to63(high priority) that corresponds to a binary DSCP bit set -
An ASCII standard name for a binary DSCP bit set
Enter ? to display the list of valid codepoint entries.
The DSCP value you enter must be currently associated with an 802.1p priority in the DSCP Policy table. The 802.1p priority and determines the packet's queue in the outbound port to which it is sent. If the packet leaves the switch on a tagged port, it carries the 802.1p priority with it to the next downstream device.
The default DSCP codepoint is
No-override. The DSCP codepoint is not overwritten in matching packets.The
noform of the command deletes the specified UDP or TCP port number or range of port numbers as a QoS classifier. If you configured a range of port numbers as the QoS classifier, you must enter the entire range in thenocommand; you cannot remove part of a range.
-
Syntax:
-
| Port Applications | DSCP Policies | |
|---|---|---|
| DSCP | Priority | |
| 23-UDP | 000111 | 7 |
| 80-TCP | 000101 | 5 |
| 914-TCP | 000010 | 1 |
| 1001-UDP | 000010 | 1 |
-
Determine whether the DSCP codepoints that you want to use to mark matching packets already have an 802.1p priority assigned, which could indicate use by existing applications (
show qos dscp-map
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.gif)
NOTE: A DSCP codepoint must also have a priority configured before you can use it to mark matching packets.
Viewing the current DSCP-map configuration
HP Switch(config)#: show qos dscp-map DSCP -> 802.p priority mappings NOTE: ‘qos type-of-service diff-services’ must be configured before DSCP is honored on inbound traffic. DSCP CodePoint DSCP Value 802.1p tag DSCP Policy name -------------- ---------- ----------- --------------------------- 000000 0 0 cs0 000001 1 No-override 000010 2 No-override 000011 3 No-override 000100 4 No-override 000101 5 No-override 000110 6 No-override 000111 7 No-override 001000 8 1 cs1 001001 9 No-override -
Configure the DSCP policies for the codepoints you want to use.
-
Assign the DSCP policies to the selected TCP/UDP port applications and display the result.
The switch applies the DSCP policies in Configuring a DSCP policy for global TCP/UDP port classifiers to IP packets with the specified TCP/UDP port applications that are received in the switch. The switch manages the packets as follows:
-
Overwrites the original DSCPs in the selected packets with the new DSCPs specified in the above policies.
-
Assigns the 802.1p priorities in the above policies to the selected packets.
-
The preceding section describes how to forward an 802.1p priority level set by an edge (or upstream) switch. This section describes how to use a global IP-Diffserv classifier to mark matching packets with a new DSCP policy. A DSCP policy consists of a DSCP codepoint and an associated 802.1p priority.
You can use a global IP-Diffserv classifier to mark a DSCP policy at the same time with a global IP-Diffserv classifier that marks an 802.1p priority if different DSCP codepoints are configured with each classifier.
To use a global IP-Diffserv classifier to mark matching packets with a new DSCP policy, follow these steps:
-
Identify the DSCP used to set a policy in packets received from an upstream or edge switch.
-
Create a new policy by using the
qos dscp-mapcommand to configure an 802.1p priority for the codepoint you will use to overwrite the DSCP that the packet carries from upstream.code-pointpriority0 - 7 -
Use the
qos type-of-service diff-servicescommand to change the policy on packets coming from the edge or upstream switch with the specified incoming DSCP.incoming-DSCPdscpoutgoing-DSCPInterior switch B honors the policy established in edge switch A illustrates this scenario.
Syntax:
Syntax:
Configures the switch to select an incoming IP packet carrying the
and then use thecurrent-codepointto assign a new, previously configured DSCP policy to the packet. The policy overwrites thenew-codepointwith thecurrent-codepointand assigns the 802.1p priority specified by the policy.new-codepointValid values for a DSCP codepoint are as follows:
A binary value for the six-bit codepoint from
000000to111111.A decimal value from
0(low priority) to63(high priority) that corresponds to a binary DSCP bit setAn ASCII standard (hexadecimal) name for a binary DSCP bit set
Enter
?to display the list of valid codepoint entries.To reconfigure the 802.1p priority currently assigned to a DSCP codepoint, use the
qos dscp-mapcommand.
Syntax:
Disables all ToS classifier operation. Current ToS DSCP policies and priorities remain in the configuration and will become available if you re-enable ToS Diff-services.
Syntax:
Deletes the DSCP policy assigned to the
and returns thecodepointto the 802.1p priority setting it had before the DSCP policy was assigned, which is either a value from 0 - 7 orcodepointNo-override.
Syntax:
Displays a listing of codepoints with any corresponding DSCP policy reassignments for outbound packets. Also displays the 802.1p priority for each codepoint that does not have a DSCP policy assigned to it.
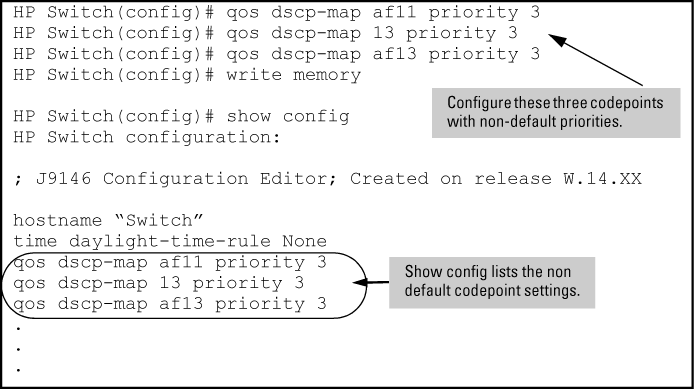
Configuring new DSCP policies
The following example shows how to configure new DSCP policies on matching packets with the specified DSCP codepoints.
-
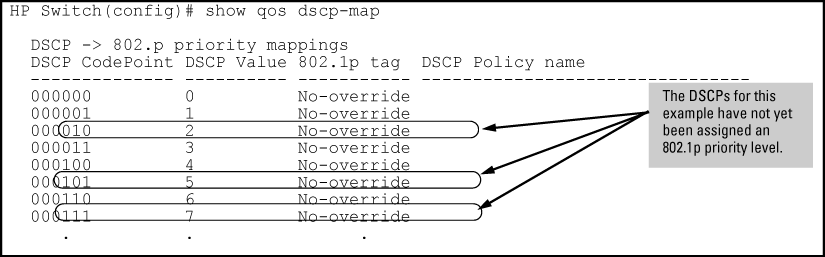
Determine if the DSCP codepoints that you want to use to mark matching packets already have an 802.1p priority assigned, which could indicate use by existing applications (
show qos dscp-map)Also, note that a DSCP codepoint must have a preconfigured 802.1p priority (0 - 7) before you can use the codepoint to mark matching packets. If a codepoint you want to use shows
No-overridein the Priority column of the DSCP Policy table (show qos dscp-mapcommand), you must first configure a priority for the codepoint before proceeding (qos dscp-map prioritycommand). -
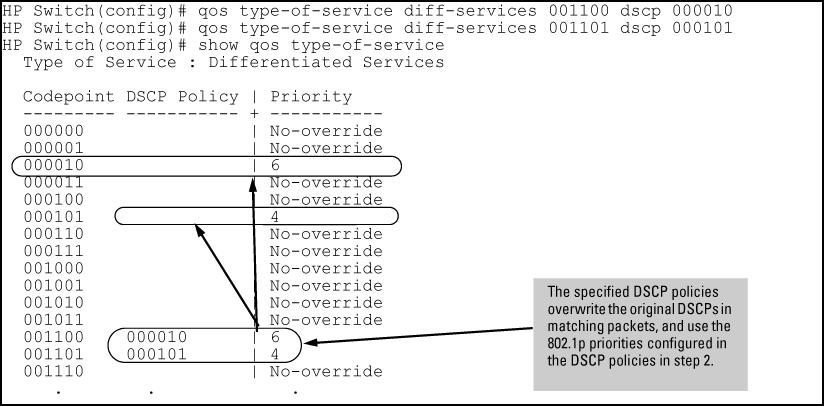
Configure the desired policies (codepoint and associated 802.1p priority) in the DSCP table:
Configuring DSCP policies in the DSCP table
HP Switch(config)#: qos dscp-map 000010 priority 6 name 'Level 6' HP Switch(config)#: qos dscp-map 000101 priority 4 name 'Level 4' HP Switch(config)#: show qos dscp-map DSCP -> 802.p priority mappings DSCP policy 802.1p tag Policy name ----------- ---------- ----------------- 000000 No-override 000001 No-override 000010 6 Level 6 000011 No-override 000100 No-override 000101 4 Level 4 000110 No-override 000111 No-override
-
Assign the new policies to mark matching packets with the specified codepoints.
This global QoS packet-marking option assigns a previously configured DSCP policy (codepoint and 802.1p priority) to outbound IP packets having the specified VLAN-ID (VID). The switch:
This global QoS packet-marking option assigns a previously configured DSCP policy (codepoint and 802.1p priority) to outbound IP packets received from the specified source-ports. The switch:
See the error messages in the following table to troubleshoot an error condition that results from reconfiguring a DSCP policy.
Error messages generated by DSCP policy changes
| Error message | Description |
|---|---|
DSCP Policy decimal-codepoint not configured |
You have tried to configure a codepoint in a global or classifier-based QoS policy for which there is no associated priority (No-override). Use the qos dscp-map command to configure a priority for the codepoint, then re-enter the codepoint in the QoS configuration. |
Cannot modify DSCP Policy codepoint - in use by other qos rules. |
You have tried to configure a codepoint in a global or classifier-based QoS policy that is already in use by other QoS policies. Before remapping the codepoint to a new priority, you must first reconfigure the other QoS policies so that they do not use the current codepoint-priority mapping. You can have multiple QoS policies that use the same codepoint to mark packets as long as it is acceptable for all such policies to use the same 802.1p priority. |
The DSCP Policy Table associates an 802.1p priority with a DSCP codepoint in an IPv4/IPv6 packet. Using DSCP codepoints in your network allows you to set a LAN policy that operates independently of 802.1Q VLAN-tagging.
In the default state, most of the 64 codepoints do not assign an 802.1p priority, as indicated by No-override in The default DSCP policy table. However, some codepoints, such as Assured Forwarding and Expedited Forwarding, have a default 802.1p priority setting.
Use the following commands to display the DSCP Policy table, configure the codepoint-priority assignments, and assign optional names to the codepoints.
Syntax:
Removes the currently configured 802.1p priority that is associated with the specified
codepointand displays theNo-overridesetting. The codepoint policy name, if configured, is also removed.
The default DSCP policy table
| DSCP Policy | 802.1p Priority | DSCP Policy | 802.1p Priority | DSCP Policy | 802.1p Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
000000 000001 000010 000011 000100 000101 000110 000111 001000 001001 001010 001011 001100 001101 001110 001111 010000 010001 010010 010011 010100 010101 |
No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override 1[a] No-override 1[a] No-override 2[a] No-override No-override No-override 0[a] No-override 0[a] No-override |
010110 010111 011000 011001 011010 011011 011100 011101 011110 011111 100000 100001 100010 100011 100100 100101 100110 100111 101000 101001 101010 |
3[a] No-override No-override No-override 4[a] No-override 4[a] No-override 5[a] No-override No-override No-override 6[a] No-override 6[a] No-override 7[a] No-override No-override No-override No-override |
101011 101100 101101 101110 101111 110000 110001 110010 110011 110100 110101 110110 110111 111000 111001 111010 111011 111100 111101 111110 111111 |
No-override No-override No-override 7[b] No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override No-override |
|
[a] Assured Forwarding codepoints; configured by default on the switches covered in this guide. [b] Expedited Forwarding codepoint configured by default. |
|||||