Any of the VLAN context commands implicitly adds a row to IgmpInterfaceTable for this VLAN if this row is missing in the table (with createAndGo for ip igmp, and createAndWait for all other commands).
You can isolate the Layer 2 traffic of different clients on same VLAN by allowing the user to assign ports to a VLAN isolate-list. An isolated port on a VLAN does not forward any Layer 2 unicast, broadcast and multicast traffic to another isolated port on same VLAN. An isolated port on a VLAN can forward any type of traffic to non-isolated port.
Syntax
NOTE: A VLAN will have only one isolate-list.
A port which is on the isolate-list for one VLAN can be in a forward-list or isolate-list for a different VLAN.
Isolate-list command
The example command allows ports a1-a4 to talk to each other on ports other than VLAN 1.
Any VLAN 1 packets received on port a1-a4 will not be forwarded to ports a1-a4. This applies to all hosts on port a1-a4, no matter if the source MAC address is authenticated or not. Additionally, there is a small window when learning a new source MAC address where packets from that address are not forwarded to ports a1-a4 dropped. Which means traffic received from a client on ports a1-a4 will not be forwarded to any other port and VLAN until the client’s MAC learned. This applies only to newly learned hosts.
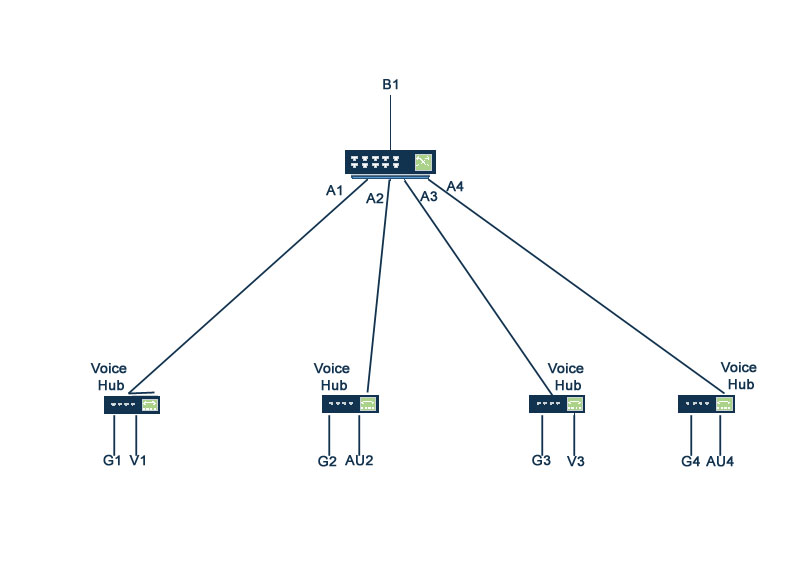
Consider Figure 1 as it represents Example 1.
Switch, user, VLAN mapping key
Designation Definition Assigned VLAN G guest users 1 V voice users 2 AU authenticated users 3 B1 uplink port A1, A2, A3, A4 ports on 2920 switch In this example, any unknown SA mac-addresses will be dropped on the ports which are in the isolate-list irrespective of the VLAN. If a switch receives a packet from a host on source-VLAN filter configured ports (isolate-list port), the packet will not be forwarded until the host’s MAC address is programmed on MAC table.
MAC table
State User Behavior Unknown SA - MAC Table is not Programmed.
Guest User
Drop on all isolate ports coming on any VLAN
Unknown SA - MAC Table is not Programmed.
Authenticated User
Drop on all isolate ports coming on any VLAN
Unknown SA - MAC Table is not Programmed.
Voice User
Drop on all isolate ports coming on any VLAN
MAC Table is Programmed.
Guest User
Drop on all isolate ports coming on the particular VLAN
MAC Table is Programmed.
Authenticated User
Forward for authenticated users.
MAC Table is Programmed.
Voice User
Forward for Voice Users.
Disables or re-enables the ability for the switch to become a querier if necessary. When changing to querier, a time delay of up to 32 seconds may occur. When no IP is assigned, the IP source address of 0.0.0.0 is used for both static (self-joined) groups and proxy queries.The “no” form of the command disables the querier function on the switch. The show ip igmp config command displays the current querier command. (Default Querier Capability: Enabled.)
Syntax
Configures the query interval. Time range is 5 to 300 seconds, the default value is 125 seconds.
Syntax
Used in the VLAN context, this command specifies how each port should handle IGMP traffic. (Default: auto.)
|
|
|
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.gif) |
NOTE: All incoming and outgoing multicast data traffic is blocked on these blocked ports including the incoming query and reports, however, the outgoing General queries are not blocked on these ports. |
|
|
Syntax
Enables igmp fast-leaves on the specified ports in the selected VLAN. The no form of the command disables igmp fast-leave on the specified ports in the selected VLAN. (Default: Enabled.)