RMON groups
Among standard RMON groups, Hewlett Packard Enterprise implements the statistics group, history group, event group, alarm group, probe configuration group, and user history group. Hewlett Packard Enterprise also implements a private alarm group, which enhances the standard alarm group. The probe configuration group and user history group are not configurable from the CLI. To configure these two groups, you must access the MIB.
Statistics group
The statistics group samples traffic statistics for monitored Ethernet interfaces and stores the statistics in the Ethernet statistics table (ethernetStatsTable). The statistics include:
Number of collisions.
CRC alignment errors.
Number of undersize or oversize packets.
Number of broadcasts.
Number of multicasts.
Number of bytes received.
Number of packets received.
The statistics in the Ethernet statistics table are cumulative sums.
History group
The history group periodically samples traffic statistics on interfaces and saves the history samples in the history table (etherHistoryTable). The statistics include:
Bandwidth utilization.
Number of error packets.
Total number of packets.
The history table stores traffic statistics collected for each sampling interval.
Event group
The event group controls the generation and notifications of events triggered by the alarms defined in the alarm group and the private alarm group. The following are RMON alarm event handling methods:
Log—Logs event information (including event time and description) in the event log table so the management device can get the logs through SNMP.
Trap—Sends an SNMP notification when the event occurs.
Log-Trap—Logs event information in the event log table and sends an SNMP notification when the event occurs.
None—Takes no actions.
Alarm group
The RMON alarm group monitors alarm variables, such as the count of incoming packets (etherStatsPkts) on an interface. After you create an alarm entry, the RMON agent samples the value of the monitored alarm variable regularly. If the value of the monitored variable is greater than or equal to the rising threshold, a rising alarm event is triggered. If the value of the monitored variable is smaller than or equal to the falling threshold, a falling alarm event is triggered. The event group defines the action to take on the alarm event.
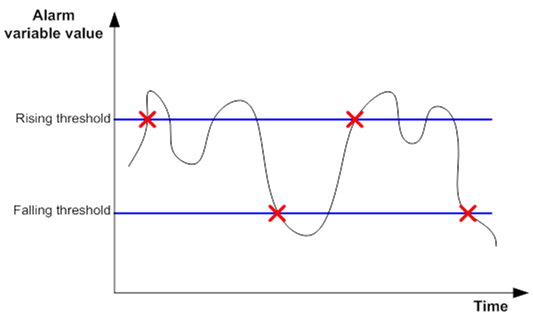
If an alarm entry crosses a threshold multiple times in succession, the RMON agent generates an alarm event only for the first crossing. For example, if the value of a sampled alarm variable crosses the rising threshold multiple times before it crosses the falling threshold, only the first crossing triggers a rising alarm event, as shown in Figure 49.
Figure 49: Rising and falling alarm events
Private alarm group
The private alarm group enables you to perform basic math operations on multiple variables, and compare the calculation result with the rising and falling thresholds.
The RMON agent samples variables and takes an alarm action based on a private alarm entry as follows:
Samples the private alarm variables in the user-defined formula.
Processes the sampled values with the formula.
Compares the calculation result with the predefined thresholds, and then takes one of the following actions:
Triggers the event associated with the rising alarm event if the result is equal to or greater than the rising threshold.
Triggers the event associated with the falling alarm event if the result is equal to or less than the falling threshold.
If a private alarm entry crosses a threshold multiple times in succession, the RMON agent generates an alarm event only for the first crossing. For example, if the value of a sampled alarm variable crosses the rising threshold multiple times before it crosses the falling threshold, only the first crossing triggers a rising alarm event.