MPLS forwarding
This section describes the MPLS forwarding information.
LFIB
An LFIB has the following table entries:
Next Hop Label Forwarding Entry (NHLFE)—Describes the label operation to be performed. It is used to forward MPLS packets.
FEC to NHLFE (FTN) map—FTN maps each FEC to a set of NHLFEs at the ingress LSR. The FTN map is used for forwarding unlabeled packets that need MPLS forwarding. When an LSR receives an unlabeled packet, it looks for the corresponding FIB entry. If the Token value of the FIB entry is not Invalid, the packet must be forwarded through MPLS. The LSR then looks for the corresponding NHLFE entry according to the Token value to determine the label operation to be performed.
Incoming Label Map (ILM)—ILM maps each incoming label to a set of NHLFEs. It is used to forward labeled packets. When an LSR receives a labeled packet, it looks for the corresponding ILM entry. If the Token value of the ILM entry is not null, the LSR looks for the corresponding NHLFE entry to determine the label operation to be performed.
FTN and ILM are associated with NHLFE through Token.
MPLS data forwarding
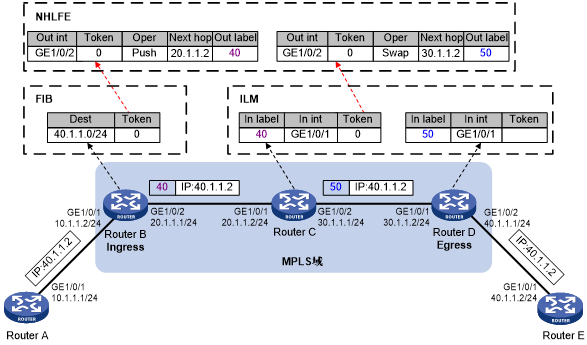
Figure 18: MPLS forwarding process diagram
In an MPLS domain, a packet is forwarded in the following procedure:
Router B (the ingress LSR) receives a packet carrying no label. It determines the FEC of the packet according to the destination address, and searches the FIB table for the Token value. Because the Token value is not Invalid, Router B looks for the corresponding NHLFE entry that contains the Token value. According to the NHLFE entry, Router B pushes label 40 to the packet, and forwards the labeled packet to the next hop LSR (Router C) through the outgoing interface (GigabitEthernet 1/0/2).
Upon receiving the labeled packet, Router C looks for the ILM entry that contains the label 40 to get the Token value. Because the Token value is not empty, Router C looks for the NHLFE entry containing the Token value. According to the NHLFE entry, Router C swaps the original label with label 50, and then forwards the labeled packet to the next hop LSR (Router D) through the outgoing interface (GigabitEthernet 1/0/2).
Upon receiving the labeled packet, Router D (the egress) looks for the ILM entry according to the label (50) to get the Token value. Because the Token is empty, Router D removes the label from the packet. If the ILM entry records the outgoing interface, Router D forwards the packet through the outgoing interface. If no outgoing interface is recorded, router D forwards the packet according to the IP header of the packet.
PHP
In an MPLS network, when an egress node receives a labeled packet, it looks up the LFIB, pops the label of the packet, and then performs the next level label forwarding or performs IP forwarding. The egress node needs to do two forwarding table lookups to forward a packet: looking up the LFIB twice or looking up the LFIB and the FIB once each.
The penultimate hop popping (PHP) feature can pop the label at the penultimate node to relieve the egress of the label operation burden.
PHP is configured on the egress node. The label assigned by a PHP-capable egress node to the penultimate hop can be one of the two listed:
IPv4 explicit null label 0—The egress assigns an IPv4 explicit null label to a FEC and advertises the FEC-label binding to the upstream LSR. When forwarding an MPLS packet, the upstream LSR replaces the label at the stack top with the explicit null label and then sends the packet to the egress. When the egress receives the packet, which carries a label of 0, it does not look up for the LFIB entry but pops the label stack directly and performs IPv4 forwarding.
Implicit null label 3—This label never appears in the label stack. An LSR directly performs a pop operation to the labeled packets that match the implicit null label rather than substituting the implicit null label for the original label at the stack top. After that, the LSR forwards the packet to the downstream egress LSR. The egress directly performs the next level forwarding upon receiving the packet.
Queue scheduling for MPLS
Queue scheduling uses a resource scheduling policy to determine the packet forwarding sequence when network congestion occurs.
To implement priority mapping and queue scheduling for packets:
In an MPLS network, you must configure the trusted packet priority type as 802.1p or DSCP for the interfaces that forward the packets on MPLS-enabled devices. For more information about priority mapping and queue scheduling, see ACL and QoS Configuration Guide.
In an MPLS L2VPN, VPLS, or MPLS L3VPN environment, you must also configure the trusted packet priority type as 802.1p or DSCP for the interfaces that forward the packets on CE devices. For more information about CE devices, see "Configuring MPLS L3VPN."