Enabling loopback detection on an Ethernet interface
If a device receives a packet that it sent, a loop has occurred to the device. Loops might cause broadcast storms, which degrade network performance. You can use this feature to detect whether a loop has occurred.
Depending on whether the receiving interface is the same as the sending interface, loops include the following types:
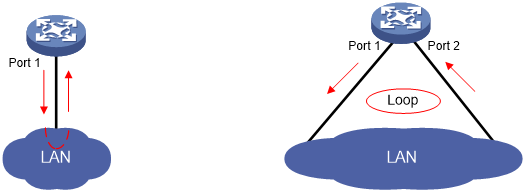
Single-port loopback—Single-port loopback occurs when an interface receives a packet that it sent and the receiving interface is the same as the sending interface, as shown in Figure 3.
Multi-port loopback—Multi-port loopback occurs when a device receives a packet that it sent but the receiving interface might not be the sending interface, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 3: Single-port loopback
Figure 4: Multi-port loopback
You can enable loopback detection to detect loops on an interface and, if the interface supports the loopback-detection action command, configure the protective action to take on the receiving interface when a loop is detected, for example, to shut down the interface. Depending on whether a protective action is configured, the device takes the actions in Table 3 to alleviate the impact of the loop condition.
Table 3: Actions to take upon detection of a loop condition
Port type | Actions | |
|---|---|---|
No protective action is configured | A protective action is configured | |
Access port |
|
|
Hybrid or trunk port |
|
|
Configuration restrictions and guidelines
To use loopback detection on an Ethernet interface, you must enable the function both globally and on the interface.
To disable loopback detection on all interfaces, run the undo loopback-detection enable command in system view.
To enable a hybrid or trunk port to take the administratively specified protective action, you must use the loopback-detection control enable command on the port.
When you change the link type of an Ethernet interface by using the port link-type command, the switch removes the protective action configured on the interface. For more information about the port link-type command, see Layer 2—LAN Switching Command Reference.
With the shutdown keyword specified, the looped port is automatically shut down and its physical state changes to Loop down. The looped port is recovered automatically after the detection interval configured by using the shutdown-interval time command. The detection interval is 30 seconds by default. For more information about the shutdown-interval time command, see Fundamentals Command Reference.
Configuration procedure
To configure loopback detection:
Step | Command | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
1. Enter system view. | system-view | N/A |
2. Enable global loopback detection. | loopback-detection enable | By default, global loopback detection is disabled. |
3. Enable multi-port loopback detection. | loopback-detection multi-port-mode enable | Optional. By default, multi-port loopback detection is disabled, and the device can only detect single-port loopback. |
4. Set the loopback detection interval. | loopback-detection interval-time time | Optional. The default setting is 30 seconds. |
5. Enter Ethernet interface view or port group view. |
| Use one of the commands. To configure loopback detection on one interface, enter Ethernet interface view. To configure loopback detection on a group of Ethernet interfaces, enter port group view. |
6. Enable loopback detection on the interface. | loopback-detection enable | By default, loopback detection is disabled. |
7. Enable loopback detection control on a trunk port or a hybrid port. | loopback-detection control enable | Optional. By default, loopback detection control is disabled. |
8. Enable loopback detection in all the VLANs on the trunk or hybrid port. | loopback-detection per-vlan enable | Optional. By default, a trunk or hybrid port performs loopback detection only in its PVID. |
9. Set the protective action to take on the interface when a loop is detected. | loopback-detection action { no-learning | semi-block | shutdown } | Optional. By default, when a loop is detected on an interface, the interface does not receive or send packets, and the system generates traps and log messages and deletes all MAC address entries of the interface. |