IPv6 addresses
IPv6 address format
An IPv6 address is represented as a set of 16-bit hexadecimals separated by colons. An IPv6 address is divided into eight groups, and each 16-bit group is represented by four hexadecimal numbers, for example, 2001:0000:130F:0000:0000:09C0:876A:130B.
To simplify the representation of IPv6 addresses, you can handle zeros in IPv6 addresses by using the following methods:
The leading zeros in each group can be removed. For example, the previous address can be represented in a shorter format as 2001:0:130F:0:0:9C0:876A:130B.
If an IPv6 address contains two or more consecutive groups of zeros, they can be replaced by a double colon (::). For example, the previous address can be represented in the shortest format as 2001:0:130F::9C0:876A:130B.
A double colon may appear once or not at all in an IPv6 address. This limit allows the device to determine how many zeros the double colon represents, and correctly convert it to zeros to restore a 128-bit IPv6 address.
An IPv6 address consists of an address prefix and an interface ID, both of which are equivalent to the network ID and the host ID of an IPv4 address, respectively.
An IPv6 address prefix is written in IPv6-address/prefix-length notation where the IPv6-address is represented in any of the formats previously mentioned and the prefix-length is a decimal number indicating how many leftmost bits of the IPv6 address comprises the address prefix.
IPv6 address types
IPv6 addresses fall into the following types:
Unicast address—An identifier for a single interface, similar to an IPv4 unicast address. A packet sent to a unicast address is delivered to the interface identified by that address.
Multicast address—An identifier for a set of interfaces (typically belonging to different nodes), similar to an IPv4 multicast address. A packet sent to a multicast address is delivered to all interfaces identified by that address.
Anycast address—An identifier for a set of interfaces (typically belonging to different nodes). A packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to the nearest one of the interfaces identified by that address. The nearest interface is chosen according to the routing protocols' measure of distance.
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: There are no broadcast addresses in IPv6. Their function is replaced by multicast addresses. | |
The type of an IPv6 address is designated by the first several bits, the format prefix. Table 6 lists the mappings between address types and format prefixes.
Table 6: Mappings between address types and format prefixes
Type | Format prefix (binary) | IPv6 prefix ID | |
|---|---|---|---|
Unicast address | Unspecified address | 00...0 (128 bits) | ::/128 |
Loopback address | 00...1 (128 bits) | ::1/128 | |
Link-local address | 1111111010 | FE80::/10 | |
Site-local address | 1111111011 | FEC0::/10 | |
Global unicast address | Other forms | N/A | |
Multicast address | 11111111 | FF00::/8 | |
Anycast address | Anycast addresses use the unicast address space and have the identical structure of unicast addresses. | ||
Unicast addresses
Unicast addresses comprise global unicast addresses, link-local unicast addresses, site-local unicast addresses, the loopback address, and the unspecified address.
Global unicast addresses, equivalent to public IPv4 addresses, are provided for network service providers. This type of address allows efficient prefix aggregation to restrict the number of global routing entries.
Link-local addresses are used for communication among link-local nodes for neighbor discovery and stateless autoconfiguration. Packets with link-local source or destination addresses are not forwarded to other links.
Site-local unicast addresses are similar to private IPv4 addresses. Packets with site-local source or destination addresses are not forwarded out of the local site (or a private network).
A loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 (or ::1). It cannot be assigned to any physical interface and can be used by a node to send an IPv6 packet to itself in the same way as the loopback address in IPv4.
An unspecified address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 (or ::). It cannot be assigned to any node. Before acquiring a valid IPv6 address, a node fills this address in the source address field of IPv6 packets. The unspecified address cannot be used as a destination IPv6 address.
Multicast addresses
IPv6 multicast addresses listed in Table 7 are reserved for special purposes.
Table 7: Reserved IPv6 multicast addresses
Address | Application |
|---|---|
FF01::1 | Node-local scope all-nodes multicast address |
FF02::1 | Link-local scope all-nodes multicast address |
FF01::2 | Node-local scope all-routers multicast address |
FF02::2 | Link-local scope all-routers multicast address |
Multicast addresses also include solicited-node addresses. A node uses a solicited-node multicast address to acquire the link-layer address of a neighboring node on the same link and to detect duplicate addresses. Each IPv6 unicast or anycast address has a corresponding solicited-node address. The format of a solicited-node multicast address is: FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FFXX:XXXX where FF02:0:0:0:0:1:FF is fixed and consists of 104 bits, and XX:XXXX is the last 24 bits of an IPv6 unicast address or anycast address.
EUI-64 address-based interface identifiers
An interface identifier is 64 bits and uniquely identifies an interface on a link.
Interfaces generate EUI-64 address-based interface identifiers differently.
On an IEEE 802 interface (such as a VLAN interface)
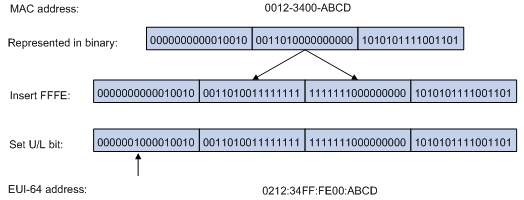
The interface identifier is derived from the link-layer address (typically a MAC address) of the interface. The MAC address is 48 bits long. To obtain an EUI-64 address-based interface identifier, you must insert the hexadecimal number FFFE (16 bits of 1111111111111110) into the MAC address (behind the 24th high-order bit), and set the universal/local (U/L) bit (which is the seventh high-order bit) to 1, to make sure that the obtained EUI-64 address-based interface identifier is globally unique.
Figure 53 shows how an EUI-64 address-based interface identifier is generated from a MAC address.
Figure 53: Converting a MAC address into an EUI-64 address-based interface identifier
On a tunnel interface
The lower 32 bits of the EUI-64 address-based interface identifier are the source IPv4 address of the tunnel interface. The higher 32 bits of the EUI-64 address-based interface identifier of an ISATAP tunnel interface are 0000:5EFE, whereas those of other tunnel interfaces are all zeros. For more information about tunnels, see "Configuring tunneling."
On an interface of another type
The EUI-64 address-based interface identifier is generated randomly by the device.