DNS proxy
A DNS proxy forwards DNS requests and replies between DNS clients and a DNS server.
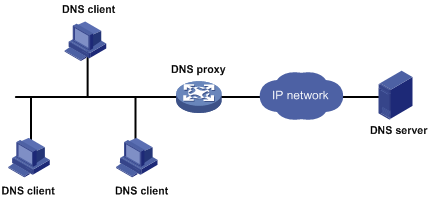
As shown in Figure 41, a DNS client sends a DNS request to the DNS proxy, which forwards the request to the designated DNS server, and conveys the reply from the DNS server to the client.
The DNS proxy simplifies network management. When the DNS server address is changed, you can change the configuration on only the DNS proxy instead of on each DNS client.
Figure 41: DNS proxy networking application
A DNS proxy operates as follows:
A DNS client considers the DNS proxy as the DNS server, and sends a DNS request to the DNS proxy. The destination address of the request is the IP address of the DNS proxy.
The DNS proxy searches the local static domain name resolution table and dynamic domain name resolution table after receiving the request. If the requested information is found, the DNS proxy returns a DNS reply to the client.
If the requested information is not found, the DNS proxy sends the request to the designated DNS server for domain name resolution.
After receiving a reply from the DNS server, the DNS proxy records the IP address-to-domain name mapping and forwards the reply to the DNS client.
With no DNS server or route to a DNS server specified, the DNS proxy does not forward DNS requests, or answer requests from the DNS clients.