IS-IS area
Two-level hierarchy
IS-IS has a two-level hierarchy to support large scale networks. A large scale routing domain is divided into multiple Areas. Typically, a Level-1 router is deployed within an area, a Level-2 router is deployed between areas, and a Level-1-2 router is deployed between Level-1 and Level-2 routers.
Level-1 and Level-2
Level-1 router—A Level-1 router establishes neighbor relationships with Level-1 and Level-1-2 routers in the same area. The LSDB maintained by the Level-1 router contains the local area routing information. It directs the packets destined for an outside area to the nearest Level-1-2 router.
Level-2 router—A Level-2 router establishes neighbor relationships with the Level-2 and Level-1-2 routers in the same or in different areas. It maintains a Level-2 LSDB containing inter-area routing information. All the Level-2 and Level-1-2 routers must be contiguous to form the backbone of a routing domain.
Level-1-2 router—A router with both Level-1 and Level-2 router functions is a Level-1-2 router. It can establish Level-1 neighbor relationships with the Level-1 and Level-1-2 routers in the same area, or establish Level-2 neighbor relationships with the Level-2 and Level-1-2 routers in different areas. A Level-1 router must be connected to other areas through a Level-1-2 router. The Level-1-2 router maintains two LSDBs, where the Level-1 LSDB is for routing within the area, and the Level-2 LSDB is for routing between areas.
The Level-1 routers in different areas cannot establish neighbor relationships.
The neighbor relationship establishment of Level-2 routers has nothing to do with area.
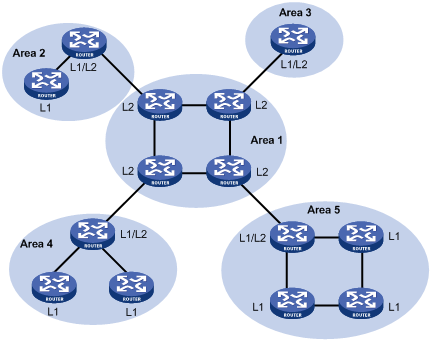
Figure 50 shows an IS-IS network topology. Area 1 comprises a set of Level-2 routers and is the backbone. The other four areas are non-backbone areas connected to the backbone through Level-1-2 routers.
Figure 50: IS-IS topology 1
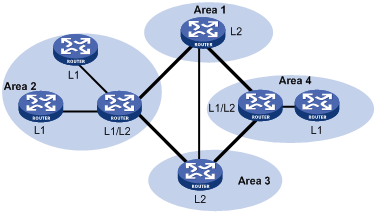
Figure 51 is another IS-IS topology. The Level-1-2 routers connect to the Level-1 and Level-2 routers, and form the IS-IS backbone together with the Level-2 routers. No area is defined as the backbone in this topology. The backbone comprises all contiguous Level-2 and Level-1-2 routers, which can reside in different areas.
Figure 51: IS-IS topology 2
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: The IS-IS backbone does not need to be a specific area. | |
Both the Level-1 and Level-2 routers use the SPF algorithm to generate the shortest path tree (SPT).
Route leaking
An IS-IS routing domain is comprised of only one Level-2 area and multiple Level-1 areas. A Level-1 area consists of a group of Level-1 routers, and is connected with a Level-2 area rather than other Level-1 areas.
The routing information of a Level-1 area is sent to the Level-2 area through the Level-1-2 router; therefore, the Level-2 router knows the routing information of the entire IS-IS routing domain. But the Level-1-2 router does not share the information of other Level-1 areas and the Level-2 area with the Level-1 area by default.
Because a Level-1 router simply sends packets destined for other areas to the nearest Level-1-2 router, the best paths may not be selected. To resolve this problem, route leaking was introduced. A Level-2 router can advertise Level-2 routing information to a specified Level-1 area. By having the routing information of other areas, a Level-1 router in the area can make a better routing decision for a packet to another area.