BGP AS number substitution and SoO attribute
BGP detects routing loops by examining AS numbers. If EBGP runs between PE and CE, you must assign different AS numbers to geographically different sites or configure the BGP AS number substitution feature to ensure correct transmission of routing information.
The BGP AS number substitution feature allows geographically different CEs to use the same AS number. If the AS_PATH of a route contains the AS number of a CE, the PE replaces the AS number with its own AS number before advertising the route to that CE.
After you enable the BGP AS number substitution feature, the PE performs BGP AS number substitution for all routes and re-advertises them to connected CEs in the peer group.
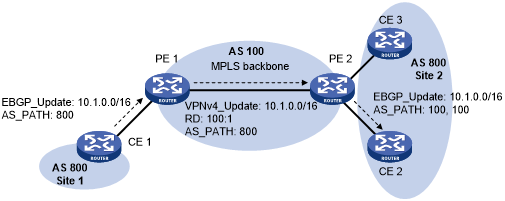
Figure 61: Application of BGP AS number substitution and SoO attribute
As shown in Figure 61, both Site 1 and Site 2 use the AS number 800. AS number substitution is enabled on PE 2 for CE 2. Before advertising updates received from CE 1 to CE 2, PE 2 substitutes its own AS number 100 for the AS number 800. In this way, CE 2 can correctly receive the routing information from CE 1.
However, the AS number substitution feature also introduces a routing loop in Site 2 because route updates originated from CE 3 can be advertised back to Site 2 through PE 2 and CE 2. To remove the routing loop, you can configure the same SoO attribute on PE 2 for CE 2 and CE 3. PE 2 adds the SoO attribute to route updates received from CE 2 or CE 3, and checks the SoO attribute of route updates to be advertised to CE 2 or CE 3. The SoO attribute of the route updates from CE 3 is the same as the SoO attribute for CE 2, and PE 2 does not advertise route updates to CE 2.
For more information about the SoO attribute, see Layer 3—IP Routing Configuration Guide.