MPLS L3VPN networking schemes
In MPLS L3VPNs, route target attributes are used to control the advertisement and reception of VPN routes between sites. They work independently and can be configured with multiple values to support flexible VPN access control and implement multiple types of VPN networking schemes.
Basic VPN networking scheme
In the simplest case, all users in a VPN form a closed user group. They can forward traffic to each other but cannot communicate with any user outside the VPN.
For the basic VPN networking scheme, you must assign a route target to each VPN for identifying the export target attribute and import target attribute of the VPN. Moreover, this route target cannot be used by any other VPNs.
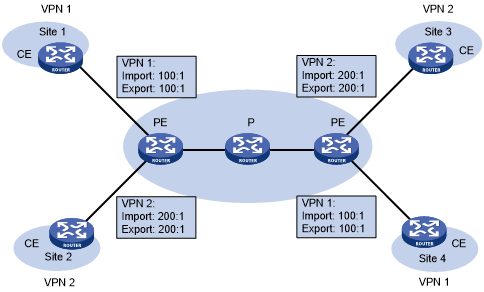
Figure 46: Network diagram for basic VPN networking scheme
As shown in Figure 46, the route target for VPN 1 is 100:1, while that for VPN 2 is 200:1. The two VPN 1 sites can communicate with each other, and the two VPN 2 sites can communicate with each other. However, the VPN 1 sites cannot communicate with the VPN 2 sites.
Hub and spoke networking scheme
The hub and spoke networking scheme is suitable for a VPN where all users must communicate with each other through an access control device.
In a hub and spoke network as shown in Figure 47, configure route targets as follows:
On spoke PEs (PEs connected to spoke sites), set the export target to Spoke and the import target to Hub.
On the hub PE (PE connected to the hub site), use two interfaces that each belong to a different VPN instance to connect the hub CE. One VPN instance receives routes from spoke PEs and has the import target set to Spoke. The other VPN instance advertises routes to spoke PEs and has the export target set to Hub.
These route targets rules produce the following results:
The hub PE can receive all VPN-IPv4 routes from spoke PEs.
All spoke PEs can receive VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by the hub PE.
The hub PE advertises the routes learned from a spoke PE to the other spoke PEs so the spoke sites can communicate with each other through the hub site.
The import target attribute of a spoke PE is different from the export target attribute of any other spoke PE. Any two spoke PEs do not directly advertise VPN-IPv4 routes to each other. Therefore, they cannot directly access each other.
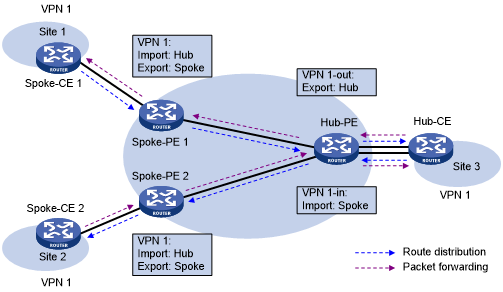
Figure 47: Network diagram for hub and spoke network
A route in Site 1 is advertised to Site 2 by using the following process:
Spoke-CE 1 advertises a route in Site 1 to Spoke-PE 1.
Spoke-PE 1 changes the route to a VPN-IPv4 route and advertises the VPN-IPv4 route to Hub-PE through MP-BGP.
Hub-PE adds the VPN-IPv4 route into the routing table of VPN 1-in, changes it to the original IPv4 route, and advertises the IPv4 route to Hub-CE.
Hub-CE advertises the IPv4 route back to Hub-PE.
Hub-PE adds the IPv4 route to the routing table of VPN 1-out, changes it to a VPN-IPv4 route, and advertises the VPN-IPv4 route to Spoke-PE 2 through MP-BGP.
Spoke-PE 2 changes the VPN-IPv4 route to the original IPv4 route, and advertises the IPv4 route to Site 2.
After spoke sites exchange routes through the hub site, they can communicate with each other through the hub site.
Extranet networking scheme
The extranet networking scheme allows specific resources in a VPN to be accessed by users not in the VPN.
In this networking scheme, if a VPN instance needs to access a shared site, the export target attribute and the import target attribute of the VPN instance must be contained in the import target attribute and the export target attribute of the VPN instance of the shared site, respectively.
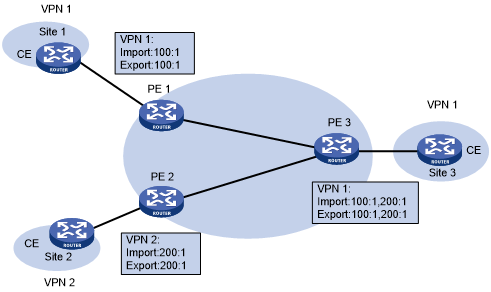
Figure 48: Network diagram for extranet networking scheme
As shown in Figure 48, route targets configured on PEs produce the following results:
PE 3 can receive VPN-IPv4 routes from PE 1 and PE 2.
PE 1 and PE 2 can receive VPN-IPv4 routes advertised by PE 3.
Site 1 and Site 3 of VPN 1 can communicate with each other, and Site 2 of VPN 2 and Site 3 of VPN 1 can communicate with each other.
PE 3 advertises neither the VPN-IPv4 routes received from PE 1 to PE 2 nor the VPN-IPv4 routes received from PE 2 to PE 1 (routes learned from an IBGP neighbor are not advertised to any other IBGP neighbor). Therefore, Site 1 of VPN 1 and Site 2 of VPN 2 cannot communicate with each other.