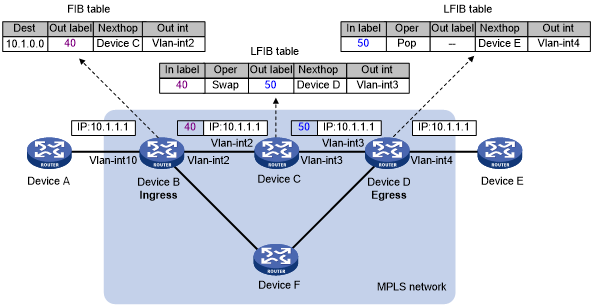
MPLS forwarding
As shown in Figure 5, a packet is forwarded over the MPLS network as follows:
Device B (the ingress LSR) receives a packet with no label. Then, it performs the following operations:
Identifies the FIB entry that matches the destination address of the packet.
Adds the outgoing label (40, in this example) to the packet.
Forwards the labeled packet out of the interface VLAN-interface 2 to the next hop LSR Device C.
When receiving the labeled packet, Device C processes the packet as follows:
Identifies the LFIB entry that has an incoming label of 40.
Uses the outgoing label 50 of the entry to replace label 40 in the packet.
Forwards the labeled packet out of the outgoing interface VLAN-interface 3 to the next hop LSR Device D.
When receiving the labeled packet, Device D (the egress LSR) processes the packet as follows:
Identifies the LFIB entry that has an incoming label of 50.
Removes the label from the packet.
Forwards the packet out of the outgoing interface VLAN-interface 4 to the next hop LSR Device E.
If the LFIB entry records no outgoing interface or next hop information, Device D performs the following operations:
Identifies the FIB entry by the IP header.
Forwards the packet according to the FIB entry.
Figure 5: MPLS forwarding