IPsec RRI
As shown in Figure 93, the traffic between the enterprise center and the branches are protected by IPsec. The gateway at the enterprise center is configured with static routes to route traffic to the IPsec-protected interfaces. It is difficult to add or modify static routes on the gateway at the enterprise center if the IPsec VPN has a large number of branches or if the network structure changes.
Figure 92: IPsec VPN
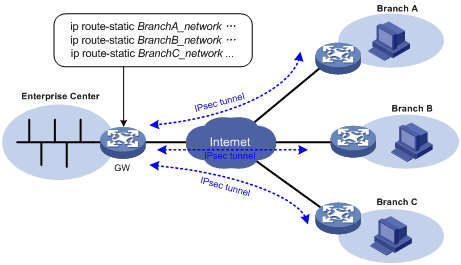
IPsec Reverse Route Injection (RRI) enables an IPsec tunnel gateway to automatically add static routes destined for protected private networks or static routes destined for peer IPsec tunnel gateways to a routing table. As shown in Figure 93, you can enable IPsec RRI on the gateway at the enterprise center. After an IPsec tunnel is established, the gateway automatically adds a static route to the routing table, which can be looked up. The destination IP address is the protected private network, and the next hop is the remote IP address of the IPsec tunnel. The traffic destined for the peer end is routed to the IPsec tunnel interface and thereby protected by IPsec.
You can advertise the static routes created by IPsec RRI in the internal network, and the internal network device can use them to forward traffic in the IPsec VPN.
In an MPLS L3VPN network, IPsec RRI can add static routes to VPN instances' routing tables.
IPsec RRI is applicable to gateways that must provide many IPsec tunnels (for example, a headquarters gateway).