DNS client verification
The DNS client verification feature protects DNS servers against DNS flood attacks. It is configured on the device where packets from the DNS clients to the DNS servers pass through. The device with DNS client verification feature configured is called a DNS client authenticator.
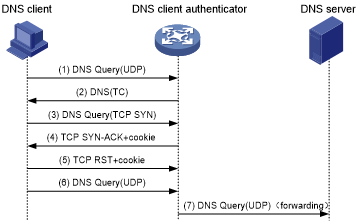
As shown in Figure 186, the DNS client verification functions as follows:
Upon receiving a UDP DNS query destined for a protected server, the DNS client authenticator responds with a DNS truncate (TC) packet. The DNS truncate packet requires the client to initiate a query in a TCP packet.
When the authenticator receives a DNS query in a TCP SYN packet to port 53 from the client, the authenticator responds with a SYN-ACK packet that contains an incorrect sequence number.
When the authenticator receives a RST packet from the client, the authenticator verifies the client as legitimate.
The authenticator adds the client's IP address to the trusted IP list and forwards the trusted client's subsequent packets to the server.
Figure 181: DNS client verification process
The DNS client verification feature requires that clients use the standard TCP/IP protocol suite and DNS protocol. Legitimate clients that use non-standard protocols will be verified as illegitimate by the DNS client authenticator.
With client verification, the first DNS resolution takes more time than normal DNS resolution.