Configuring portal server detection and portal user synchronization
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 72, the host is directly connected to the router (the access device). The host is assigned a public IP address either manually or through DHCP. A portal server acts as both a portal authentication server and a portal Web server. A RADIUS server acts as the authentication/accounting server.
Configure direct portal authentication on the router, so the host can access only the portal server before passing the authentication and access other network resources after passing the authentication.
Configure the router to do the following:
Detect the reachability state of the portal authentication server.
Send log messages upon state changes.
Disable portal authentication when the authentication server is unreachable.
Synchronize portal user information with the portal server periodically.
Figure 65: Network diagram
Configuration prerequisites and guidelines
Configure IP addresses for the router and servers as shown in Figure 72 and make sure the host, router, and servers can reach each other.
Configure the RADIUS server correctly to provide authentication and accounting functions.
Configure the portal authentication server. Be sure to enable the server heartbeat function and the user heartbeat function.
Configure the router (access device) as follows:
Configure direct portal authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2, the interface to which the host is connected.
Configure portal authentication server detection, so that the router can detect the reachability of the portal authentication server by cooperating with the portal server heartbeat function.
Configure portal user synchronization, so that the router can synchronize portal user information with the portal authentication server by cooperating with the portal user heartbeat function.
Configuring the portal authentication server on IMC PLAT 5.0
In this example, the portal server runs on IMC PLAT 5.0(E0101) and IMC UAM 5.0(E0101).
Configure the portal authentication server:
Log in to IMC and click the Service tab.
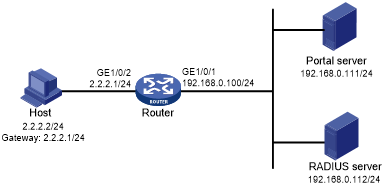
Select User Access Manager > Portal Service Management > Server from the navigation tree to open the portal server configuration page as shown in Figure 73.
Configure the portal server heartbeat interval and user heartbeat interval.
Use the default settings for other parameters.
Click OK.
Figure 66: Portal authentication server configuration
Configure the IP address group:
Select User Access Manager > Portal Service Management > IP Group from the navigation tree to open the portal IP address group configuration page.
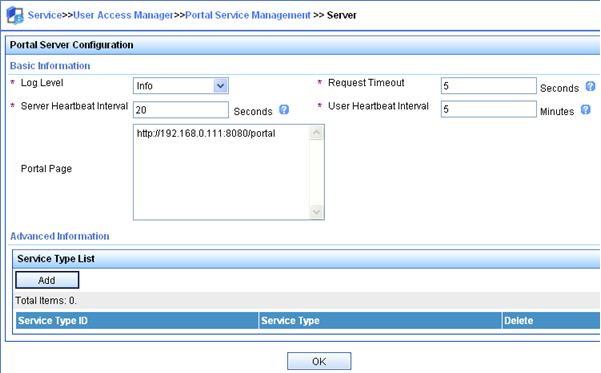
Click Add to open the page as shown in Figure 74.
Enter the IP group name.
Enter the start IP address and end IP address of the IP group.
Make sure the host IP address is in the IP group.
Select a service group.
This example uses the default group Ungrouped.
Select Normal from the Action list.
Click OK.
Figure 67: Adding an IP address group
Add a portal device:
Select User Access Manager > Portal Service Management > Device from the navigation tree to open the portal device configuration page.
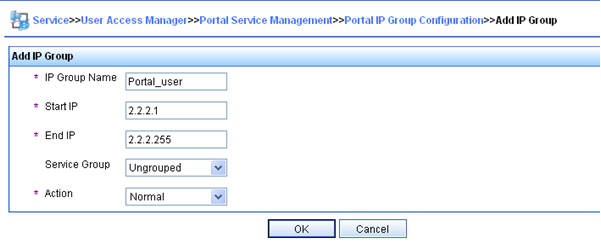
Click Add to open the page as shown in Figure 75.
Enter the device name NAS.
Enter the IP address of the router's interface connected to the host.
Enter the key, which must be the same as that configured on the router.
Set whether to enable IP address reallocation.
This example uses direct portal authentication, and therefore select No from the Reallocate IP list.
Select whether to support sever heartbeat and user heartbeat functions.
In this example, select Yes for both Support Server Heartbeat and Support User Heartbeat.
Click OK.
Figure 68: Adding a portal device
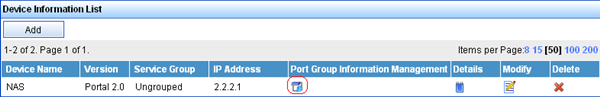
Associate the portal device with the IP address group:
As shown in Figure 76, click the icon in the Port Group Information Management column of device NAS to open the port group configuration page.
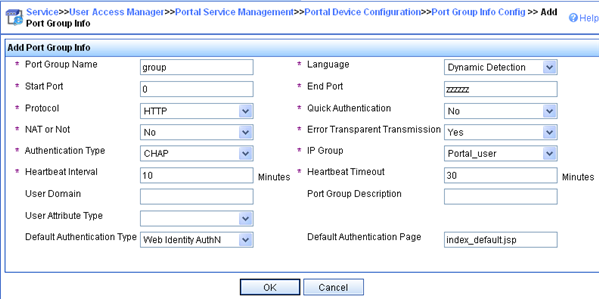
Click Add to open the page as shown in Figure 77.
Enter the port group name.
Select the configured IP address group.
The IP address used by the user to access the network must be within this IP address group.
Use the default settings for other parameters.
Click OK.
Figure 69: Device list
Figure 70: Adding a port group
Configuring the portal authentication server on IMC PLAT 7.1
In this example, the portal server runs on IMC PLAT 7.1(E0303) and IMC EIA 7.1(F0303).
Configure the portal authentication server:
Log in to IMC and click the User tab.
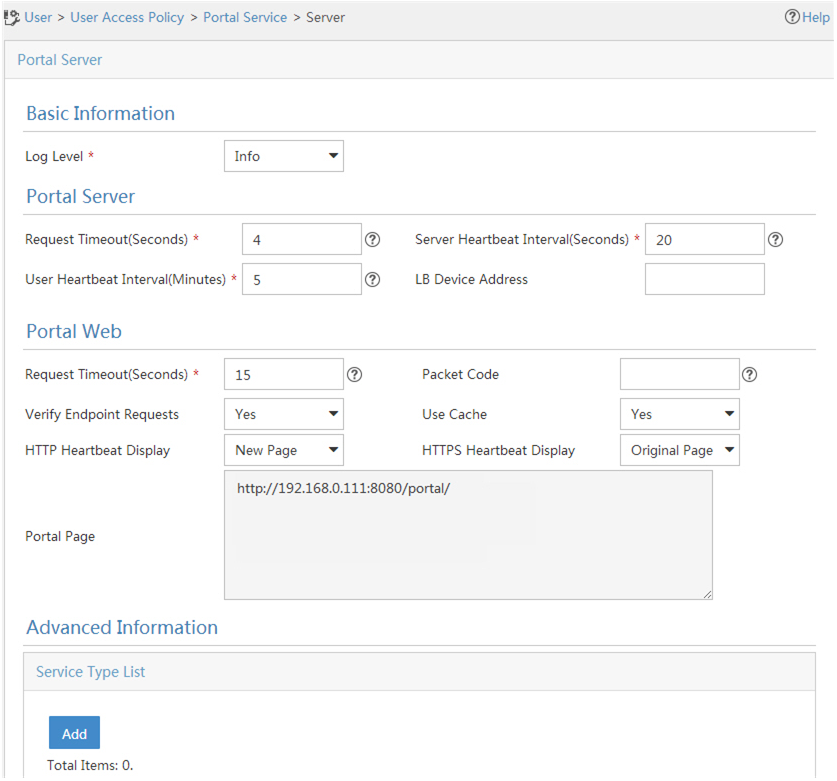
Select User Access Policy > Portal Service > Server from the navigation tree to open the portal server configuration page, as shown in Figure 78.
Configure the portal server parameters as needed.
This example uses the default settings.
Click OK.
Figure 71: Portal authentication server configuration
Configure the IP address group:
Select User Access Policy > Portal Service > IP Group from the navigation tree to open the portal IP address group configuration page.
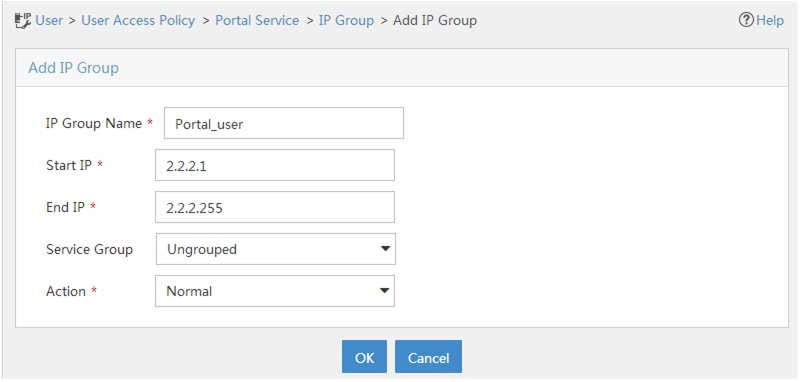
Click Add to open the page as shown in Figure 79
Enter the IP group name.
Enter the start IP address and end IP address of the IP group.
Make sure the client IP address (2.2.2.2) is in the IP group.
Select a service group.
This example uses the default group Ungrouped.
Select Normal from the Action list.
Click OK.
Figure 72: Adding an IP address group
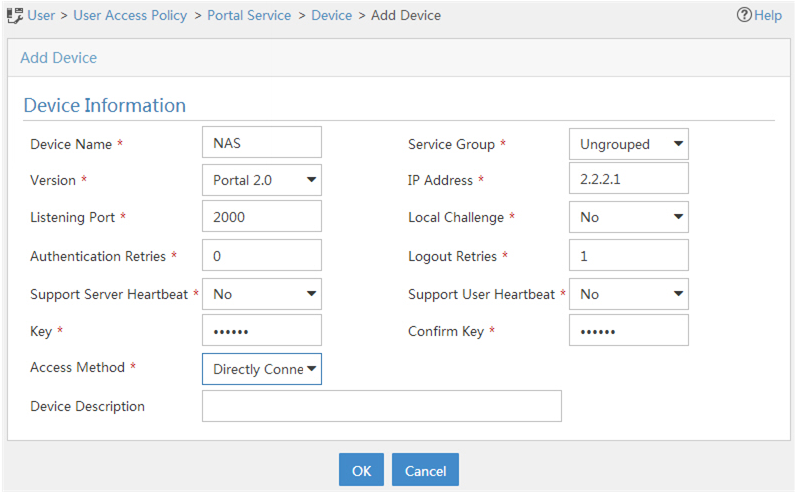
Add a portal device:
Select User Access Policy > Portal Service > Device from the navigation tree to open the portal device configuration page.
Click Add to open the page as shown inFigure 80
Enter the device name NAS.
Enter the IP address of the router's interface connected to the host.
Enter the key, which must be the same as that configured on the router.
Select Directly Connected for Access Method in this example.
Set whether to support the portal server heartbeat and user heartbeat functions.
In this example, select No for both Support Server Heartbeat and Support User Heartbeat.
Click OK.
Figure 73: Adding a portal device
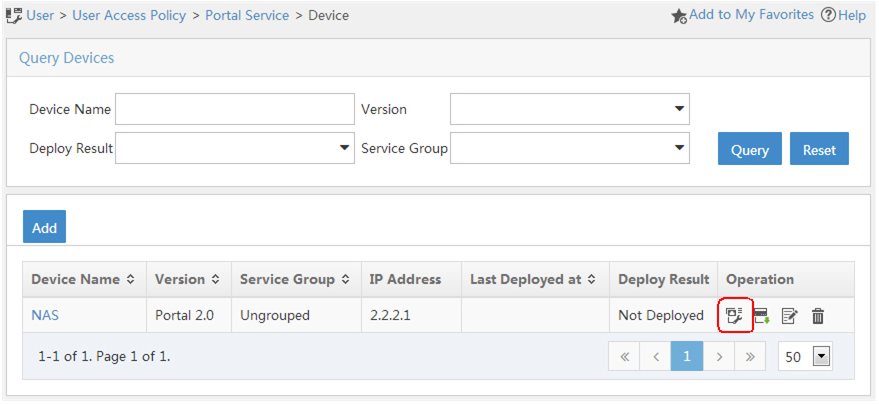
Associate the portal device with the IP address group:
As shown in Figure 81click the Port Group Information Management icon for device NAS to open the port group configuration page.
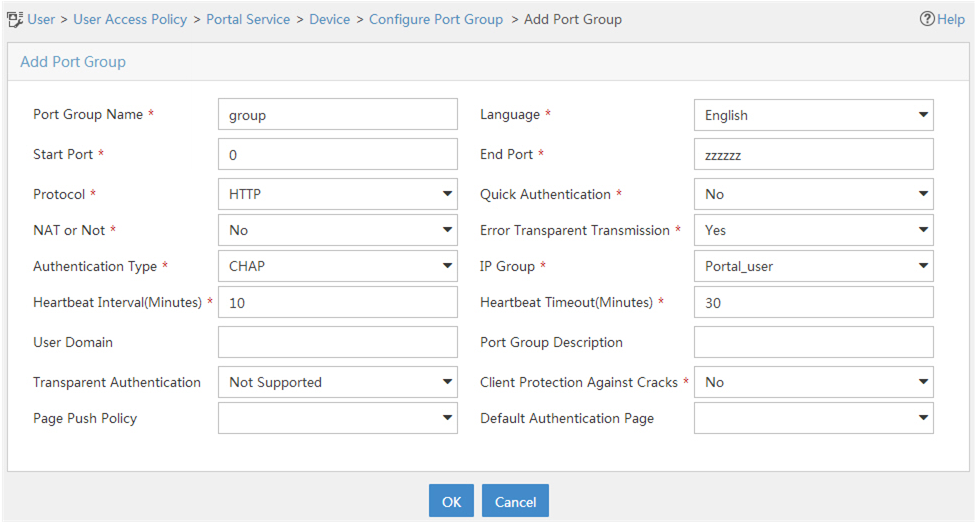
Click Add to open the page as shown in Figure 82
Enter the port group name.
Select the configured IP address group.
The IP address used by the user to access the network must be within this IP address group.
Use the default settings for other parameters.
Click OK.
Figure 74: Device list
Figure 75: Adding a port group
Configuring the router
Configure a RADIUS scheme:
# Create a RADIUS scheme named rs1 and enter its view.
<Router> system-view [Router] radius scheme rs1
# Specify the primary authentication server and primary accounting server, and configure the keys for communication with the servers.
[Router-radius-rs1] primary authentication 192.168.0.112 [Router-radius-rs1] primary accounting 192.168.0.112 [Router-radius-rs1] key authentication simple radius [Router-radius-rs1] key accounting simple radius
# Exclude the ISP domain name from the username sent to the RADIUS server.
[Router-radius-rs1] user-name-format without-domain [Router-radius-rs1] quit
# Enable RADIUS session control.
[Router] radius session-control enable
Configure an authentication domain:
# Create an ISP domain named dm1 and enter its view.
[Router] domain dm1
# Configure AAA methods for the ISP domain.
[Router-isp-dm1] authentication portal radius-scheme rs1 [Router-isp-dm1] authorization portal radius-scheme rs1 [Router-isp-dm1] accounting portal radius-scheme rs1 [Router-isp-dm1] quit
# Configure domain dm1 as the default ISP domain. If a user enters the username without the ISP domain name at login, the authentication and accounting methods of the default domain are used for the user.
[Router] domain default enable dm1
Configure portal authentication:
# Configure a portal authentication server.
[Router] portal server newpt [Router-portal-server-newpt] ip 192.168.0.111 key simple portal [Router-portal-server-newpt] port 50100
# Configure reachability detection of the portal authentication server: set the server detection interval to 40 seconds, and send log messages upon reachability status changes.
[Router-portal-server-newpt] server-detect timeout 40 log
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png)
NOTE:
The value of timeout must be greater than or equal to the portal server heartbeat interval.
# Configure portal user synchronization with the portal authentication server, and set the synchronization detection interval to 600 seconds.
[Router-portal-server-newpt] user-sync timeout 600 [Router-portal-server-newpt] quit
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png)
NOTE:
The value of timeout must be greater than or equal to the portal user heartbeat interval.
# Configure a portal Web server.
[Router] portal web-server newpt [Router-portal-websvr-newpt] url http://192.168.0.111:8080/portal [Router-portal-websvr-newpt] quit
# Enable direct portal authentication on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[Router] interface gigabitethernet 1/0/2 [Router–GigabitEthernet1/0/2] portal enable method direct
# Enable portal fail-permit for the portal authentication server newpt.
[Router–GigabitEthernet1/0/2] portal fail-permit server newpt
# Reference the portal Web server newpt on GigabitEthernet 1/0/2.
[Router–GigabitEthernet1/0/2] portal apply web-server newpt
# Configure the BAS-IP as 2.2.2.1 for portal packets sent from GigabitEthernet 1/0/2 to the portal authentication server.
[Router–GigabitEthernet1/0/2] portal bas-ip 2.2.2.1 [Router–GigabitEthernet1/0/2] quit
Verifying the configuration
# Use the following command to display information about the portal authentication server.
[Router] display portal server newpt Portal server: newpt Type : IMC IP : 192.168.0.111 VPN instance : Not configured Port : 50100 Server Detection : Timeout 40s Action: log User synchronization : Timeout 600s Status : Up
The Up status of the portal authentication server indicates that the portal authentication server is reachable. If the access device detects that the portal authentication server is unreachable, the Status field in the command output displays Down. The access device generates a server unreachable log "Portal server newpt turns down from up." and disables portal authentication on the access interface, so the host can access the external network without authentication.