Basic concepts
LLDP agent
An LLDP agent is a mapping of an entity where LLDP runs. Multiple LLDP agents can run on the same interface.
LLDP agents are divided into the following types:
Nearest bridge agent.
Nearest customer bridge agent.
Nearest non-TPMR bridge agent.
A Two-port MAC Relay (TPMR) is a type of bridge that has only two externally-accessible bridge ports. It supports a subset of the features of a MAC bridge. A TPMR is transparent to all frame-based media-independent protocols except for the following protocols:
Protocols destined to it.
Protocols destined to reserved MAC addresses that the relay feature of the TPMR is configured not to forward.
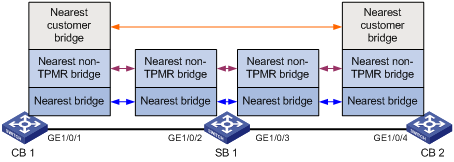
LLDP exchanges packets between neighbor agents and creates and maintains neighbor information for them. Figure 47 shows the neighbor relationships for these LLDP agents. LLDP has two bridge modes: customer bridge (CB) and service bridge (SB).
Figure 47: LLDP neighbor relationships
LLDP frame formats
LLDP sends device information in LLDP frames. LLDP frames are encapsulated in Ethernet II or Subnetwork Access Protocol (SNAP) frames.
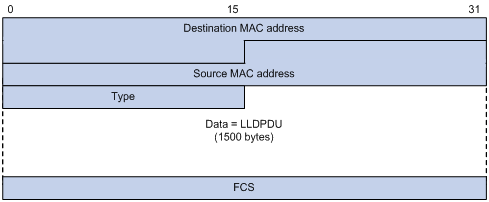
LLDP frame encapsulated in Ethernet II
Figure 48: Ethernet II-encapsulated LLDP frame
Table 13: Fields in an Ethernet II-encapsulated LLDP frame
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Destination MAC address | MAC address to which the LLDP frame is advertised. LLDP specifies different multicast MAC addresses as destination MAC addresses for LLDP frames destined for agents of different types. This helps distinguish between LLDP frames sent and received by different agent types on the same interface. The destination MAC address is fixed to one of the following multicast MAC addresses:
|
Source MAC address | MAC address of the sending port. |
Type | Ethernet type for the upper-layer protocol. This field is 0x88CC for LLDP. |
Data | LLDPDU. |
FCS | Frame check sequence, a 32-bit CRC value used to determine the validity of the received Ethernet frame. |
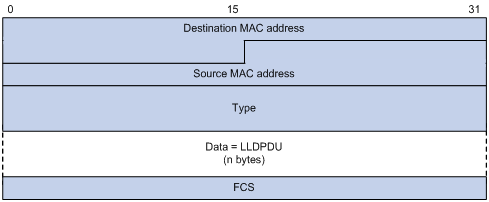
LLDP frame encapsulated in SNAP
Figure 49: SNAP-encapsulated LLDP frame
Table 14: Fields in a SNAP-encapsulated LLDP frame
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Destination MAC address | MAC address to which the LLDP frame is advertised. It is the same as that for Ethernet II-encapsulated LLDP frames. |
Source MAC address | MAC address of the sending port. |
Type | SNAP type for the upper-layer protocol. This field is 0xAAAA-0300-0000-88CC for LLDP. |
Data | LLDPDU. |
FCS | Frame check sequence, a 32-bit CRC value used to determine the validity of the received Ethernet frame. |
LLDPDUs
LLDP uses LLDPDUs to exchange information. An LLDPDU comprises multiple TLVs. Each TLV carries a type of device information, as shown in Figure 50.
Figure 50: LLDPDU encapsulation format
An LLDPDU can carry up to 32 types of TLVs. Mandatory TLVs include Chassis ID TLV, Port ID TLV, and Time to Live TLV. Other TLVs are optional.
TLVs
A TLV is an information element that contains the type, length, and value fields.
LLDPDU TLVs include the following categories:
Basic management TLVs
Organizationally (IEEE 802.1 and IEEE 802.3) specific TLVs
LLDP-MED (media endpoint discovery) TLVs
Basic management TLVs are essential to device management.
Organizationally specific TLVs and LLDP-MED TLVs are used for enhanced device management. They are defined by standardization or other organizations and are optional for LLDPDUs.
Basic management TLVs
Table 15 lists the basic management TLV types. Some of them are mandatory for LLDPDUs.
Table 15: Basic management TLVs
Type
Description
Remarks
Chassis ID
Specifies the bridge MAC address of the sending device.
Mandatory.
Port ID
Specifies the ID of the sending port:
If the LLDPDU carries LLDP-MED TLVs, the port ID TLV carries the MAC address of the sending port.
Otherwise, the port ID TLV carries the port name.
Time to Live
Specifies the life of the transmitted information on the receiving device.
End of LLDPDU
Marks the end of the TLV sequence in the LLDPDU.
Optional.
Port Description
Specifies the description for the sending port.
System Name
Specifies the assigned name of the sending device.
System Description
Specifies the description for the sending device.
System Capabilities
Identifies the primary features of the sending device and the enabled primary features.
Management Address
Specifies the following elements:
The management address of the local device.
The interface number and object identifier (OID) associated with the address.
IEEE 802.1 organizationally specific TLVs
Table 16: IEEE 802.1 organizationally specific TLVs
Type
Description
Port VLAN ID (PVID)
Specifies the port VLAN identifier.
Port And Protocol VLAN ID (PPVID)
Indicates whether the device supports protocol VLANs and, if so, what VLAN IDs these protocols will be associated with.
VLAN Name
Specifies the textual name of any VLAN to which the port belongs.
Protocol Identity
Indicates protocols supported on the port.
Link Aggregation
Indicates whether the port supports link aggregation, and if yes, whether link aggregation is enabled.
Management VID
Management VLAN ID.
VID Usage Digest
VLAN ID usage digest.
ETS Configuration
Enhanced Transmission Selection configuration.
ETS Recommendation
ETS recommendation.
PFC
Priority-based Flow Control.
APP
Application protocol.
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: HPE devices support only receiving protocol identity TLVs and VID usage digest TLVs. Layer 3 Ethernet ports support only link aggregation TLVs. | |
IEEE 802.3 organizationally specific TLVs
Table 17: IEEE 802.3 organizationally specific TLVs
Type
Description
MAC/PHY Configuration/Status
Contains the bit-rate and duplex capabilities of the port, support for autonegotiation, enabling status of autonegotiation, and the current rate and duplex mode.
Power Via MDI
Contains the power supply capabilities of the port:
Port class (PSE or PD).
Power supply mode.
Whether PSE power supply is supported.
Whether PSE power supply is enabled.
Whether pair selection can be controlled.
Power supply type.
Power source.
Power priority.
PD requested power.
PSE allocated power.
Maximum Frame Size
Indicates the supported maximum frame size.
Power Stateful Control
Indicates the power state control configured on the sending port, including the following:
Power supply mode of the PSE/PD.
PSE/PD priority.
PSE/PD power.
Energy-Efficient Ethernet
Indicates Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE).
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: The Power Stateful Control TLV is defined in IEEE P802.3at D1.0 and is not supported in later versions. HPE devices send this type of TLVs only after receiving them. | |
LLDP-MED TLVs
LLDP-MED TLVs provide multiple advanced applications for voice over IP (VoIP), such as basic configuration, network policy configuration, and address and directory management. LLDP-MED TLVs provide a cost-effective and easy-to-use solution for deploying voice devices in Ethernet. LLDP-MED TLVs are shown in Table 18.
Table 18: LLDP-MED TLVs
Type
Description
LLDP-MED Capabilities
Allows a network device to advertise the LLDP-MED TLVs that it supports.
Network Policy
Allows a network device or terminal device to advertise the VLAN ID of a port, the VLAN type, and the Layer 2 and Layer 3 priorities for specific applications.
Extended Power-via-MDI
Allows a network device or terminal device to advertise power supply capability. This TLV is an extension of the Power Via MDI TLV.
Hardware Revision
Allows a terminal device to advertise its hardware version.
Firmware Revision
Allows a terminal device to advertise its firmware version.
Software Revision
Allows a terminal device to advertise its software version.
Serial Number
Allows a terminal device to advertise its serial number.
Manufacturer Name
Allows a terminal device to advertise its vendor name.
Model Name
Allows a terminal device to advertise its model name.
Asset ID
Allows a terminal device to advertise its asset ID. The typical case is that the user specifies the asset ID for the endpoint to facilitate directory management and asset tracking.
Location Identification
Allows a network device to advertise the appropriate location identifier information for a terminal device to use in the context of location-based applications.
![[NOTE: ]](images/note.png) | NOTE: If the MAC/PHY configuration/status TLV is not advertisable, none of the LLDP-MED TLVs will be advertised even if they are advertisable. If the LLDP-MED capabilities TLV is not advertisable, the other LLDP-MED TLVs will not be advertised even if they are advertisable. | |
Management address
The network management system uses the management address of a device to identify and manage the device for topology maintenance and network management. The management address is encapsulated in the management address TLV.